Battery Emulation
Emulate your battery
Emulating a battery during product development is crucial because it allows engineers to test devices under realistic and repeatable power conditions without relying on physical cells. Using the battery profile, which describe battery internal resistance and open-circuit voltage across discharge states, developers can accurately reproduce how the battery will behave throughout its lifecycle. This enables early validation of performance, power management, and fault handling, while avoiding the variability, cost, and time associated with cycling real batteries.
Products needed
Battery profile generated from battery profiling
How to connect
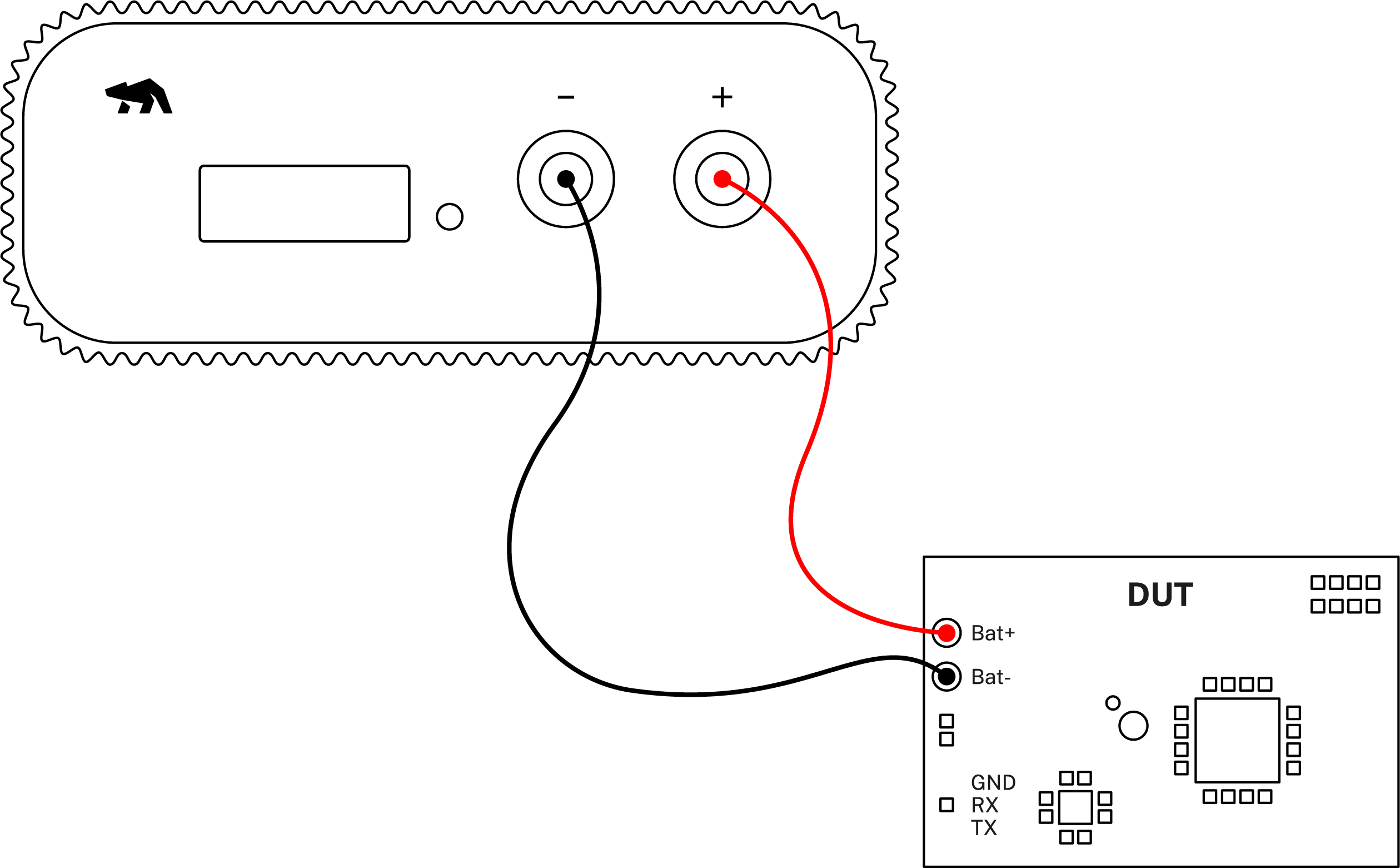
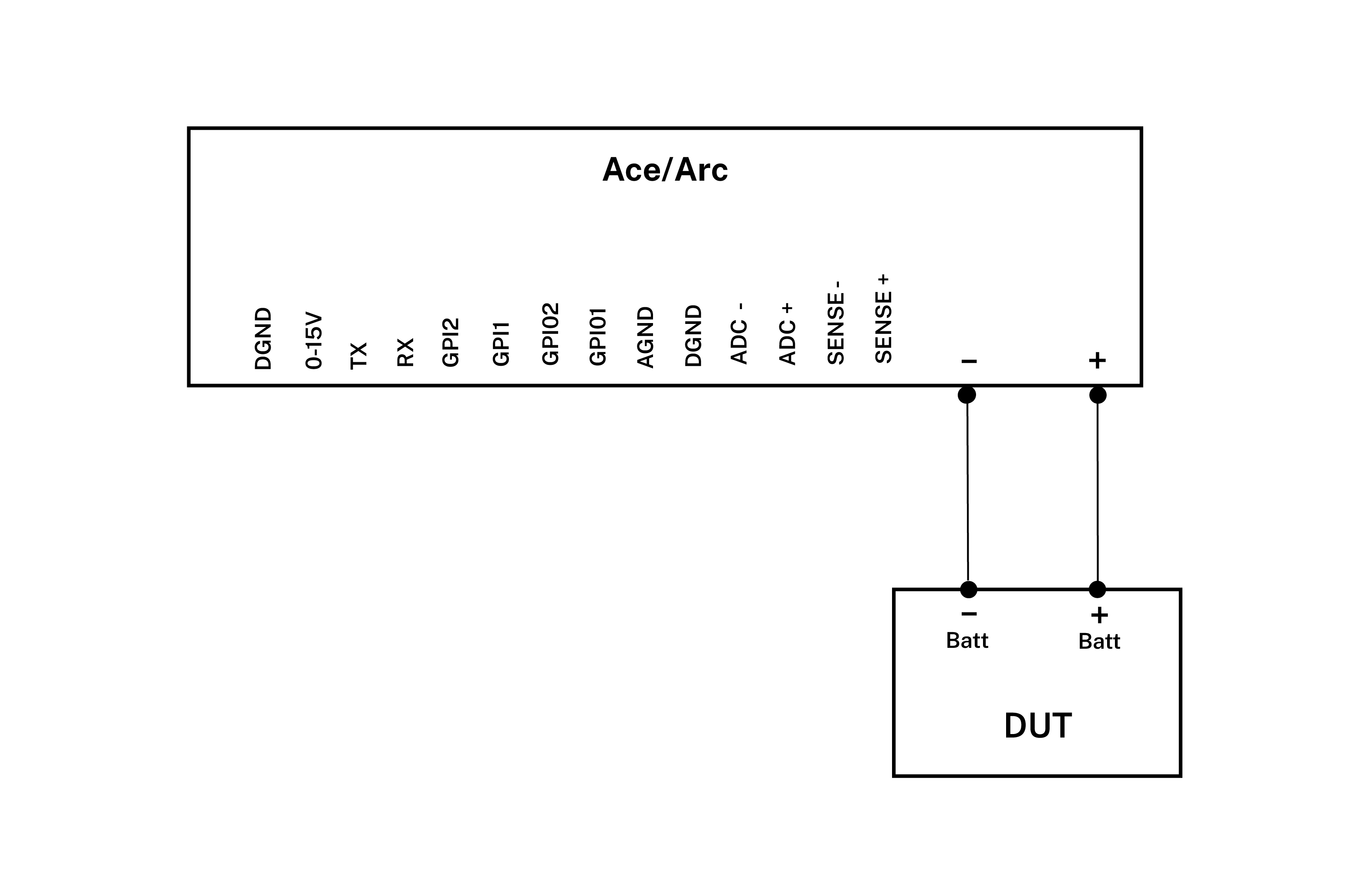
- Connect Arc/Ace to your computer by USB. If needed add a power supply.
- Connect Arc/Ace’s banana connector + to DUT positive battery connector/power connector.
- Connect Arc/Ace’s banana connector – to DUT negative battery connector/power connector GND.
- Optionally, connect for showing UART logs, subsystem measurement, GPI's, or any other of the use cases described previously.
Get started in the Otii application
- Add your Arc/Ace under Control in the sidebar. Rename it if desired (right click).
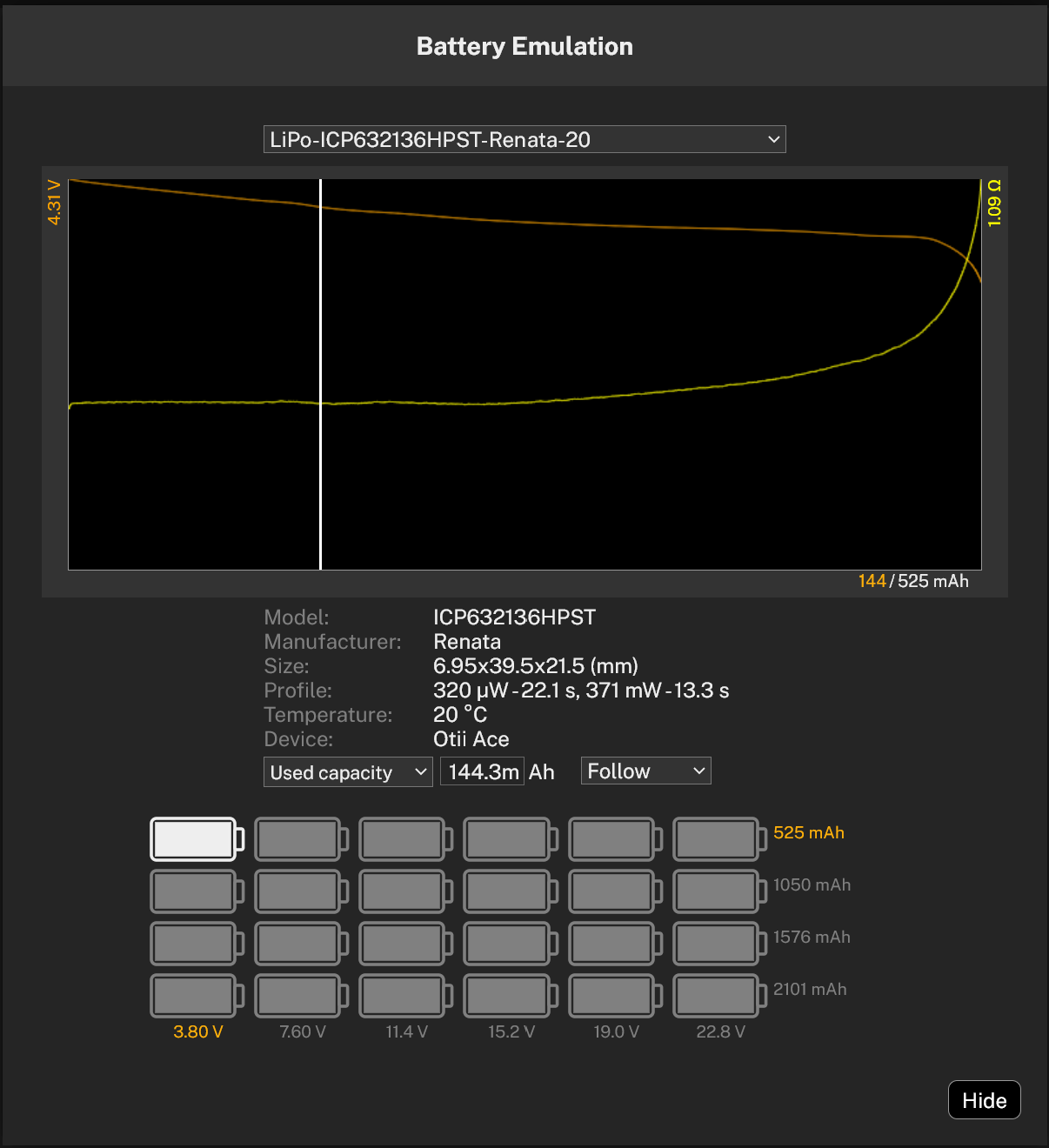
- In General Settings, select Battery Emulation
- Select the battery profile to emulate
- Optionally, select if the battery is going to be a battery pack. It is possible to have the battery in series, parallell or both.
- Click Hide
- Select if Used capacity or State Of Charge SOC (%) is going to be used.
- Select where on the discharge curve the emulation is going to be performed by either click dragging in the small graph or enter Used capacity or SOC (%) value. This can also be changed when the recording has started.
- Under Channels enable Main current, Main voltage and Main power channels. These will show as graphs.
- Optionally, enable any other channel depending on the use case, when emulating a battery.
- Start a recording. Your DUT is still not powered, and you will only see measured noise.
- Power the DUT by turn on the supply (On button) next to the Arc/Ace.
- Output voltage will now be dependent on the battery open circuit voltage, internal resistance and the load.
Tips & tricks
 Set the Used capacity/SOC far to the right in the graph, to get the DUT to reset, then change the value until you get a full active period. Note the Used capacity/SOC. This data can be used in the Battery Life Estimation tool to, more accurately, estimate the battery life.
Set the Used capacity/SOC far to the right in the graph, to get the DUT to reset, then change the value until you get a full active period. Note the Used capacity/SOC. This data can be used in the Battery Life Estimation tool to, more accurately, estimate the battery life.